Atomic Volumes for Mesh Completion
Symposium on Geometry Processing, July 2005
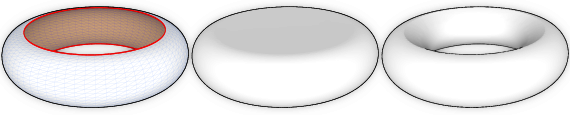
Complex holes can be filled in different manners. By constraining parts of the mesh to be inside or outside thefinal volume, our method can fill an incomplete torus (left) to produce watertight meshes with genus 0 (middle) or genus 1 (right).
Abstract
The increased use of scanned geometry for applications in computer graphics and 3D hardcopy output has highlighted
the need for general, robust algorithms for reconstruction of watertight 3D models given partial polygonal
meshes as input. We present an algorithm for 3D hole filling based on a decomposition of space into atomic volumes,
which are each determined to be either completely inside or completely outside the model. By defining the
output model as the union of interior atomic volumes we guarantee that the resulting mesh is watertight. Individual
volumes are labeled as “inside” or “outside” by computing a minimum-cost cut of a graph representation of
the atomic volume structure, patching all the holes simultaneously in a globally sensitive manner. User control
is provided to select between multiple topologically distinct, yet still valid, ways of filling holes. Finally, we use
an octree decomposition of space to provide output-sensitive computation time. We demonstrate the ability of our
algorithm to fill complex, non-planar holes in large meshes obtained from 3D scanning devices.
Paper
Video
- AVI file (19 MB, 3:45)
Talk
Acknowledgements
- Sponsored in part by software donation from Alias
Citation
Joshua Podolak and Szymon Rusinkiewicz.
"Atomic Volumes for Mesh Completion."
Symposium on Geometry Processing, July 2005.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{Podolak:2005:AVF,
author = "Joshua Podolak and Szymon Rusinkiewicz",
title = "Atomic Volumes for Mesh Completion",
booktitle = "Symposium on Geometry Processing",
year = "2005",
month = jul
}