An RGBN Benchmark
Princeton University, February 2016
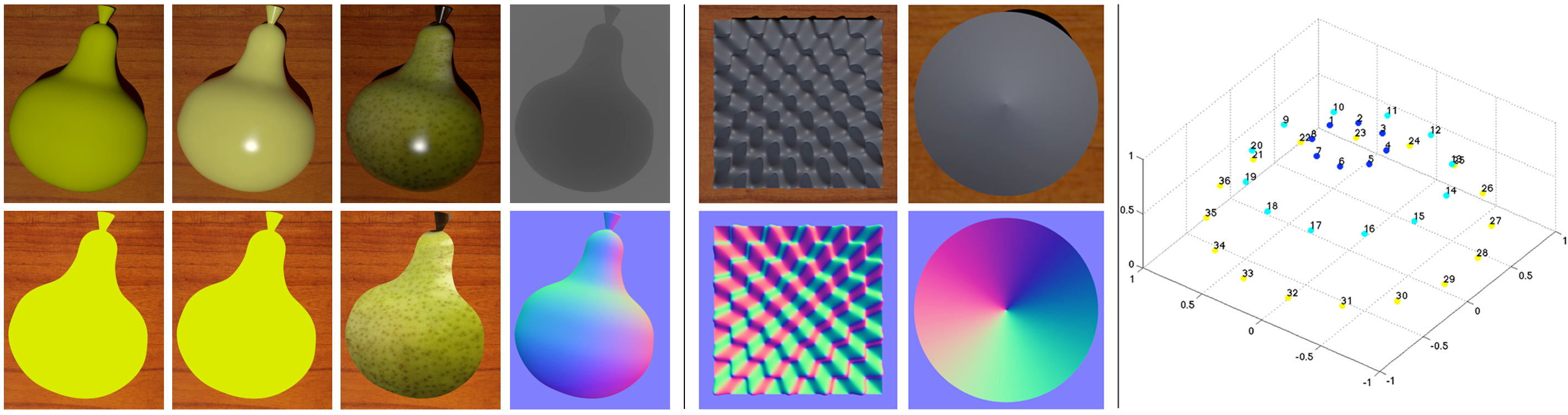
A photometric benchmark for applications such as photometric stereo.
Abstract
A variety of algorithms in both computer vision and
graphics use datasets of an object or scene captured with
fixed camera but varying illumination. Evaluating these algorithms
is frequently challenging because of the lack of
ground truth on the one hand, and insufficiently realistic
and varied synthetic datasets on the other. In this work,
we present a synthetic benchmark for applications such as
photometric stereo, and justify it by comparing to real-life
objects and their rendered models. Additionally, we introduce
a system that allows the user to create scenes by combining
arbitrary 3D models, materials, and light configurations.
The system outputs physically-based renderings as
well as dense ground-truth maps of quantities such as normals,
height map, BRDF specifications, and albedo. We
present a number of synthetic datasets which will be available
online, and we provide a few photometric datasets of
real-life objects. Our work demonstrates that real objects
can be simulated well enough so that the conclusions about
accuracy drawn from our synthetic datasets match those
based on real objects. The paper also demonstrates a use
case for this RGBN benchmark: the evaluation of photometric
stereo algorithms. We present a taxonomy of photometric
stereo techniques, investigate the causes of errors in
several of them, and propose a photometric stereo variant
that iteratively estimates shadowing.
Paper
Data
Citation
Sema Berkiten and Szymon Rusinkiewicz.
"An RGBN Benchmark."
Technical Report TR-977-16, Princeton University, February 2016.
BibTeX
@techreport{Berkiten:2016:ARB,
author = "Sema Berkiten and Szymon Rusinkiewicz",
title = "An {RGBN} Benchmark",
institution = "Princeton University",
year = "2016",
month = feb,
number = "TR-977-16"
}