Learning to Infer Semantic Parameters for 3D Shape Editing
International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), November 2020
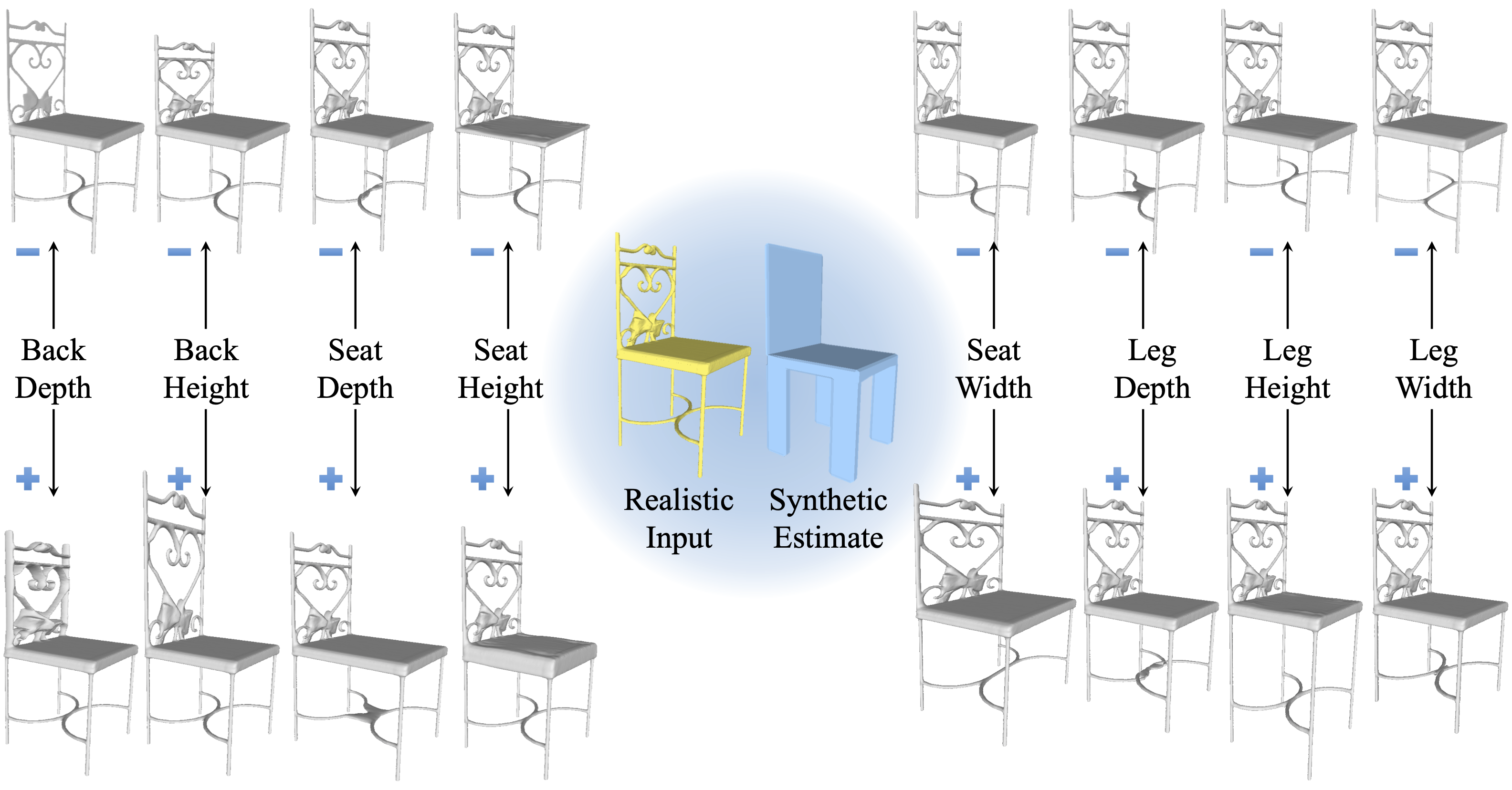
Semantic editing. Taking a realistic shape (yellow) as input, the proposed method allows for editing of different parts (gray). This is achieved by learning to infer the semantic parameters of an auxiliary synthetic shape (blue), without any labels from realistic shapes.
Abstract
Many applications in 3D shape design and augmentation require the ability to make specific edits to an object’s semantic parameters (e.g., the pose of a person’s arm or the length of an airplane’s wing) while preserving as much existing details as possible. We propose to learn a deep network that infers the semantic parameters of an input shape and then allows the user to manipulate those parameters. The network is trained jointly on shapes from an auxiliary synthetic template and unlabeled realistic models, ensuring robustness to shape variability while relieving the need to label realistic exemplars. At testing time, edits within the parameter space drive deformations to be applied to the original shape, which provides semantically-meaningful manipulation while preserving the details. This is in contrast to prior methods that either use autoencoders with a limited latent-space dimensionality, failing to preserve arbitrary detail, or drive deformations with purely-geometric controls, such as cages, losing the ability to update local part regions. Experiments with datasets of chairs, airplanes, and human bodies demonstrate that our method produces more natural edits than prior work.
Paper
Supplemental Material
Links
- This paper on arXiv
Citation
Fangyin Wei, Elena Sizikova, Avneesh Sud, Szymon Rusinkiewicz, and Thomas Funkhouser.
"Learning to Infer Semantic Parameters for 3D Shape Editing."
International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), November 2020.
BibTeX
@inproceedings{Wei:2020:LTI,
author = "Fangyin Wei and Elena Sizikova and Avneesh Sud and Szymon Rusinkiewicz
and Thomas Funkhouser",
title = "Learning to Infer Semantic Parameters for {3D} Shape Editing",
booktitle = "International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV)",
year = "2020",
month = nov
}